Direct Identification Matching Explained
The Direct Identification matching method uses lot number or serial number tracking to match an exported product with its exact importation to claim drawback. However, in the absence of lot or serial number tracing, a claimant can instead utilize one of the acceptable accounting methods.
Here’s an Example of Direct Identification Matching
Direct Identification Matching Is Used When Merchandise Does Not Qualify For HTS level Substitution
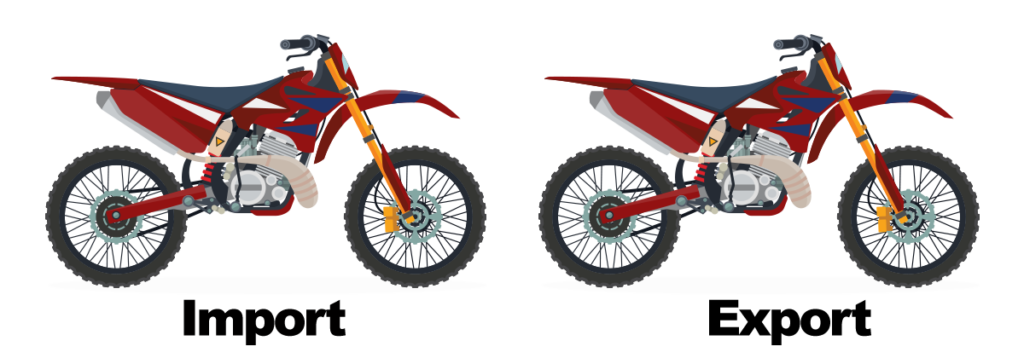
Motorbike with Serial #P4STR4N4 is imported duty paid into the United Stated and then exported to Belgium Unused
Unused Merchandise Direct ID
Provision: 19 USC 1313(j)(1)
The export is traced back to the import using lot number or serial number matching. If lot or serial numbers are not present, then the claimant must use one of the accepted accounting methods, such as FIFO or LIFO.
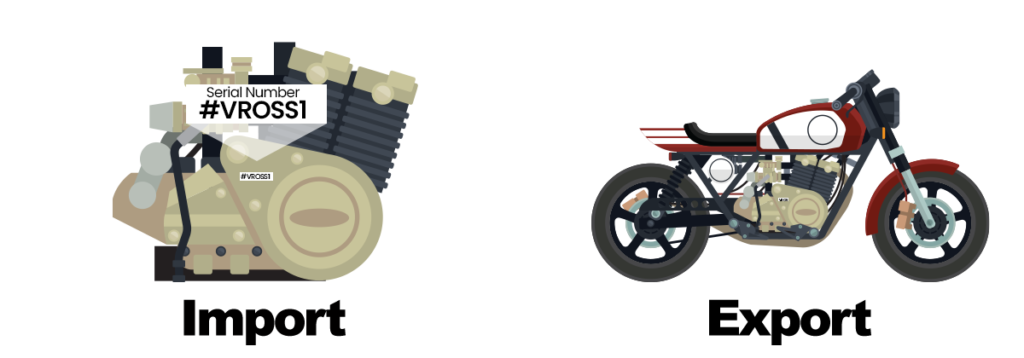
Serialized motors are imported duty paid into the United Stated, assembled into a motorcycle and then exported to Italy
Manufacturing Direct ID
Provision: 19 USC 1313(a)
Using Manufacturing Direct Identification, the imported component that is contained in the exported finished product is traced back to importation using a lot number or serial number. If imported components lose their identity when entered into inventory, then the claimant must use one of the accepted drawback accounting methods, such as FIFO or LIFO, to comply with the requirements of Direct Identification.
Direct Identification Drawback Explained Video
Watch this animated video about on Direct Identification Drawback
The Regulatory Language of Direct Identification Matching and Accounting Methods
§ 190.31 Direct identification unused merchandise drawback.
(a) General. Section 313(j)(1) of the Act, as amended (19 U.S.C. 1313(j)(1)), provides for drawback upon the exportation or destruction under CBP supervision of imported merchandise upon which was paid any duty, tax, or fee imposed under Federal law upon entry or importation, if the merchandise has not been used within the United States before such exportation or destruction. The total amount of drawback allowable will not exceed 99 percent of the amount of duties, taxes, and fees paid with respect to the imported merchandise.
(b) Time of exportation or destruction. Drawback will be allowable on imported merchandise if, before the close of the 5-year period beginning on the date of importation and before the drawback claim is filed, the merchandise is exported from the United States or destroyed under CBP supervision.
(c) Operations performed on imported merchandise. The performing of any operation or combination of operations, not amounting to manufacture or production under the provisions of the manufacturing drawback law as provided for in 19 U.S.C. 1313(j)(3), on imported merchandise is not a use of that merchandise for purposes of this section.
§ 190.21 Direct identification manufacturing drawback.
Section 313(a) of the Act, as amended (19 U.S.C. 1313(a)), provides for drawback upon the exportation, or destruction under CBP supervision, of articles manufactured or produced in the United States with the use of imported merchandise, provided that those articles have not been used in the United States prior to such exportation or destruction. The amount of drawback allowable will not exceed 99 percent of the amount of duties, taxes, and fees paid with respect to the imported merchandise. However, duties may not be refunded upon the exportation or destruction of flour or by-products produced from imported wheat. Where two or more products result, drawback must be distributed among the products in accordance with their relative values, as defined in § 190.2, at the time of separation. Merchandise may be identified for drawback purposes under 19 U.S.C. 1313(a) in the manner provided for and prescribed in § 190.14.
§ 190.14 Identification of merchandise or articles by accounting method.
(a) General. This section provides for the identification of merchandise or articles for drawback purposes by the use of accounting methods. This section applies to identification of merchandise or articles in inventory or storage, as well as identification of merchandise used in manufacture or production, as defined in § 190.2. This section is not applicable to situations in which the drawback law authorizes substitution (substitution is allowed in specified situations under 19 U.S.C. 1313(b), 1313(j)(2), 1313(k), and 1313(p); this section does apply to situations in these subsections in which substitution is not allowed, as well as to the subsections of the drawback law under which no substitution is allowed). When substitution is authorized, merchandise or articles may be substituted without reference to this section, under the criteria and conditions specifically authorized in the statutory and regulatory provisions providing for the substitution.
(b) Conditions and criteria for identification by accounting method. Manufacturers, producers, claimants, or other appropriate persons may identify for drawback purposes lots of merchandise or articles under this section, subject to each of the following conditions and criteria:
(1) The lots of merchandise or articles to be so identified must be fungible as defined in § 190.2;
(2) The person using the identification method must be able to establish that inventory records (for example, material control records), prepared and used in the ordinary course of business, account for the lots of merchandise or articles to be identified as being received into and withdrawn from the same inventory. Even if merchandise or articles are received or withdrawn at different geographical locations, if such inventory records treat receipts or withdrawals as being from the same inventory, those inventory records may be used to identify the merchandise or articles under this section, subject to the conditions of this section. If any such inventory records (that is, inventory records prepared and used in the ordinary course of business) treat receipts and withdrawals as being from different inventories, those inventory records must be used and receipts into or withdrawals from the different inventories may not be accounted for together. If units of merchandise or articles can be specifically identified (for example, by serial number), the merchandise or articles must be specifically identified and may not be identified by accounting method, unless it is established that inventory records, prepared and used in the ordinary course of business, treat the merchandise or articles to be identified as being received into and withdrawn from the same inventory (subject to the above conditions);
(3) Unless otherwise provided in this section or specifically approved by CBP (by a binding ruling under part 177 of this chapter), all receipts (or inputs) into and all withdrawals from the inventory must be recorded in the accounting record;
(4) The records which support any identification method under this section are subject to verification by CBP (see § 190.61). If CBP requests such verification, the person using the identification method must be able to demonstrate how, under generally accepted accounting procedures, the records which support the identification method used account for all merchandise or articles in, and all receipts into and withdrawals from, the inventory, and the drawback per unit for each receipt and withdrawal; and
(5) Any accounting method which is used by a person for drawback purposes under this section must be used exclusively, without using other methods for a period of at least 1 year, unless approval is given by CBP for a shorter period.
(c) Approved accounting methods. The following accounting methods are approved for use in the identification of merchandise or articles for drawback purposes under this section. If a claim is eligible for the use of any accounting method, the claimant must indicate on the drawback entry whether an accounting method was used, and if so, which accounting method was used, to identify the merchandise as part of the complete claim (see § 190.51).
(1) First-in, first-out (FIFO) – (i) General. The FIFO method is the method by which fungible merchandise or articles are identified by recordkeeping on the basis of the first merchandise or articles received into the inventory. Under this method, withdrawals are from the oldest (first-in) merchandise or articles in the inventory at the time of withdrawal.
(ii) Example. If the beginning inventory is zero, 100 units with $1 drawback attributable per unit are received in inventory on the 2nd of the month, 50 units with no drawback attributable per unit are received into inventory on the 5th of the month, 75 units are withdrawn for domestic (non-export) shipment on the 10th of the month, 75 units with $2 drawback attributable per unit are received in inventory on the 15th of the month, 100 units are withdrawn for export on the 20th of the month, and no other receipts or withdrawals occurred in the month, the drawback attributable to the 100 units withdrawn for export on the 20th is a total of $75 (25 units from the receipt on the 2nd with $1 drawback attributable per unit, 50 units from the receipt on the 5th with no drawback attributable per unit, and 25 units from the receipt on the 15th with $2 drawback attributable per unit). The basis of the foregoing and the effects on the inventory of the receipts and withdrawals, and balance in the inventory thereafter are as follows: On the 2nd of the month the receipt of 100 units ($1 drawback/unit) results in a balance of that amount; the receipt of 50 units ($0 drawback/unit) on the 5th results in a balance of 150 units (100 with $1 drawback/unit and 50 with $0 drawback/unit); the withdrawal on the 10th of 75 units ($1 drawback/unit) results in a balance of 75 units (25 with $1 drawback/unit and 50 with $0 drawback/unit); the receipt of 75 units ($2 drawback/unit) on the 15th results in a balance of 150 units (25 with $1 drawback/unit, 50 with $0 drawback/unit, and 75 with $2 drawback/unit); the withdrawal on the 20th of 100 units (25 with $1 drawback/unit, 50 with $0 drawback/unit, and 25 with $2 drawback unit) results in a balance of 50 units (all 50 with $2 drawback/unit).
(2) Last-in, first out (LIFO) – (i) General. The LIFO method is the method by which fungible merchandise or articles are identified by recordkeeping on the basis of the last merchandise or articles received into the inventory. Under this method, withdrawals are from the newest (last-in) merchandise or articles in the inventory at the time of withdrawal.
(ii) Example. In the example in paragraph (c)(1)(ii) of this section, the drawback attributable to the 100 units withdrawn for export on the 20th is a total of $175 (75 units from the receipt on the 15th with $2 drawback attributable per unit and 25 units from the receipt on the 2nd with $1 drawback attributable per unit). The basis of the foregoing and the effects on the inventory of the receipts and withdrawals, and balance in the inventory thereafter are as follows: On the 2nd of the month the receipt of 100 units ($1 drawback/unit) results in a balance of that amount; the receipt of 50 units ($0 drawback/unit) on the 5th results in a balance of 150 units (100 with $1 drawback/unit and 50 with $0 drawback/unit); the withdrawal on the 10th of 75 units (50 with $0 drawback/unit and 25 with $1 drawback/unit) results in a balance of 75 units (all with $1 drawback/unit); the receipt of 75 units ($2 drawback/unit) on the 15th results in a balance of 150 units (75 with $1 drawback/unit and 75 with $2 drawback/unit); the withdrawal on the 20th of 100 units (75 with $2 drawback/unit and 25 with $1 drawback/unit) results in a balance of 50 units (all 50 with $1 drawback/unit).
(3) Low-to-high –
(i) General. The low-to-high method is the method by which fungible merchandise or articles are identified by recordkeeping on the basis of the lowest drawback amount per unit of the merchandise or articles in inventory. Merchandise or articles with no drawback attributable to them (for example, domestic merchandise or duty-free merchandise) must be accounted for and are treated as having the lowest drawback attributable to them. Under this method, withdrawals are from the merchandise or articles with the least amount of drawback attributable to them, then those with the next higher amount, and so forth. If the same amount of drawback is attributable to more than one lot of merchandise or articles, withdrawals are from the oldest (first-in) merchandise or articles among those lots with the same amount of drawback attributable. Drawback requirements are applicable to withdrawn merchandise or articles as identified (for example, if the merchandise or articles identified were attributable to an import more than 5 years before the claimed export, no drawback could be granted).
(ii) Ordinary low-to-high –
(A) Method. Under the ordinary low-to-high method, all receipts into and all withdrawals from the inventory are recorded in the accounting record and accounted for so that each withdrawal, whether for export or domestic shipment, is identified by recordkeeping on the basis of the lowest drawback amount per unit of the merchandise or articles available in the inventory.
(iii) Low-to-high method with established average inventory turn-over period –
(A) Method. Under the low-to-high method with established average inventory turn-over period, all receipts into and all withdrawals for export are recorded in the accounting record and accounted for so that each withdrawal is identified by recordkeeping on the basis of the lowest drawback amount per available unit of the merchandise or articles received into the inventory in the established average inventory turn-over period preceding the withdrawal.
(B) Accounting for withdrawals (for domestic shipments and for export). Under the low-to-high method with established average inventory turn-over period, domestic withdrawals (withdrawals for domestic shipment) are not accounted for and do not affect the available units of merchandise or articles. All withdrawals for export must be accounted for whether or not drawback is available or claimed on the withdrawals. Once a withdrawal for export is made and accounted for under this method, the merchandise or articles withdrawn are no longer available for identification.
(C) Establishment of inventory turn-over period. For purposes of the low-to-high method with established average inventory turn-over period, the average inventory turn-over period is based on the rate of withdrawal from inventory and represents the time in which all of the merchandise or articles in the inventory at a given time must have been withdrawn based on that rate. To establish an average of this time, at least 1 year, or 3 turn-over periods (if inventory turns over fewer than 3 times per year), must be averaged. The inventory turn-over period must be that for the merchandise or articles to be identified, except that if the person using the method has more than one kind of merchandise or articles with different inventory turn-over periods, the longest average turn-over period established under this section may be used (instead of using a different inventory turn-over period for each kind of merchandise or article).
(D) Example. In the example in paragraph (c)(3)(ii)(B) of this section (but, as required for this method, without accounting for domestic withdrawals, and with an established average inventory turn-over period of 30 days), the drawback attributable to the January 15 withdrawal for export is zero (the available receipt in the preceding 30 days with the lowest amount of drawback is the January 2 receipt, of which 50 units will remain after the withdrawal), the drawback attributable to the February 5 withdrawal for export is $101.50 (the January 20 and January 25 receipts), the drawback attributable to the February 15 withdrawal for export is $47.50 (the February 10 receipt), the drawback attributable to the February 28 withdrawal for export is $51.50 (the February 20 and January 31 receipts), the drawback attributable to the March 15 withdrawal for export is $42.50 (the March 10 receipt), and the drawback attributable to the March 31 withdrawal for export is $98.00 (the March 25 and March 5 receipts). No drawback may be claimed on the basis of the January 5 receipt or the February 25 receipt because in the case of each, there were insufficient withdrawals for export within the established average inventory turn-over period; the 50 units remaining from the January 2 receipt after the January 15 withdrawal are not identified for a withdrawal for export because there is no other withdrawal for export (other than the January 15 withdrawal) within the established average inventory turn-over period; the March 20 receipt (50 units at $1.08) is not yet attributed to withdrawals for export. Total drawback attributable to withdrawals for export in this example would be $341.00.
(iv) Low-to-high blanket method –
(A) Method. Under the low-to-high blanket method, all receipts into and all withdrawals for export are recorded in the accounting record and accounted for. Each withdrawal is identified on the basis of the lowest drawback amount per available unit of the merchandise or articles received into inventory in the applicable statutory period for export preceding the withdrawal (e.g., 180 days under 19 U.S.C. 1313(p) and 5 years for other types of drawback claims pursuant to 19 U.S.C. 1313(r)). Drawback requirements are applicable to withdrawn merchandise or articles as identified (for example, no drawback could be granted generally if the merchandise or articles identified were attributable to an import made more than 5 years before the claimed export; and, for claims pursuant to 19 U.S.C. 1313(p), no drawback could be granted if the merchandise or articles identified were attributable to an import that was entered more than 180 days after the date of the claimed export or if the claimed export was more than 180 days after the close of the manufacturing period attributable to an import).
(B) Accounting for withdrawals (for domestic shipments and for export). Under the low-to-high blanket method, domestic withdrawals (withdrawals for domestic shipment) are not accounted for and do not affect the available units of merchandise or articles. All withdrawals for export must be accounted for whether or not drawback is available or claimed on the withdrawals. Once a withdrawal for export is made and accounted for under this method, the merchandise or articles withdrawn are no longer available for identification.
(C) Example. In the example in paragraph (c)(3)(ii)(B) of this section (but, as required for this method, without accounting for domestic withdrawals), the drawback attributable to the January 15 withdrawal for export is zero (the available receipt in the inventory with the lowest amount of drawback is the January 2 receipt, of which 50 units will remain after the withdrawal), the drawback attributable to the February 5 withdrawal for export is $50.00 (the remainder of the January 2 receipt and the January 5 receipt), the drawback attributable to the February 15 withdrawal for export is $47.50 (the February 10 receipt), the drawback attributable to the February 28 withdrawal for export is $50.50 (the February 20 and January 20 receipts), the drawback attributable to the March 15 withdrawal for export is $42.50 (the March 10 receipt), and the drawback attributable to the March 31 withdrawal for export is $96.00 (the March 25 and January 25 receipts). Receipts not attributed to withdrawals for export are the January 31 (50 units at $1.03), February 25 (50 units at $1.05), March 5 (50 units at $1.06), and March 20 (50 units at $1.08) receipts. Total drawback attributable to withdrawals for export in this example would be $286.50.
(4) Average –
(i) General. The average method is the method by which fungible merchandise or articles are identified on the basis of the calculation by recordkeeping of the amount of drawback that may be attributed to each unit of merchandise or articles in the inventory. In this method, the ratio of:
(A) The total units of a particular receipt of the fungible merchandise in the inventory at the time of a withdrawal to;
(B) The total units of all receipts of the fungible merchandise (including each receipt into inventory) at the time of the withdrawal;
(C) Is applied to the withdrawal, so that the withdrawal consists of a proportionate quantity of units from each particular receipt and each receipt is correspondingly decreased. Withdrawals and corresponding decreases to receipts are rounded to the nearest whole number.
(ii) Example. In the example in paragraph (c)(1)(ii) of this section, the drawback attributable to the 100 units withdrawn for export on the 20th is a total of $133 (50 units from the receipt on the 15th with $2 drawback attributable per unit, 33 units from the receipt on the 2nd with $1 drawback attributable per unit, and 17 units from the receipt on the 5th with $0 drawback attributable per unit). The basis of the foregoing and the effects on the inventory of the receipts and withdrawals, and balance in the inventory thereafter are as follows: On the 2nd of the month the receipt of 100 units ($1 drawback/unit) results in a balance of that amount; the receipt of 50 units ($0 drawback/unit) on the 5th results in a balance of 150 units (100 with $1 drawback/unit and 50 with $0 drawback/unit); the withdrawal on the 10th of 75 units (50 with $1 drawback/unit (applying the ratio of 100 units from the receipt on the 2nd to the total of 150 units at the time of withdrawal) and 25 with $0 drawback/unit (applying the ratio of 50 units from the receipt on the 5th to the total of 150 units at the time of withdrawal)) results in a balance of 75 units (with 50 with $1 drawback/unit and 25 with $0 drawback/unit, on the basis of the same ratios); the receipt of 75 units ($2 drawback/unit) on the 15th results in a balance of 150 units (50 with $1 drawback/unit, 25 with $0 drawback/unit, and 75 with $2 drawback/unit); the withdrawal on the 20th of 100 units (50 with $2 drawback/unit (applying the ratio of the 75 units from the receipt on the 15th to the total of 150 units at the time of withdrawal), 33 with $1 drawback/unit (applying the ratio of the 50 units remaining from the receipt on the 2nd to the total of 150 units at the time of withdrawal, and 17 with $0 drawback/unit (applying the ratio of the 25 units remaining from the receipt on the 5th to the total of 150 units at the time of withdrawal)) results in a balance of 50 units (25 with $2 drawback/unit, 17 with $1 drawback/unit, and 8 with $0 drawback/unit, on the basis of the same ratios).
(5) Inventory turn-over for limited purposes. A properly established average inventory turn-over period, as provided for in paragraph (c)(3)(iii)(C) of this section, may be used to determine:
(i) The fact and date(s) of use in manufacture or production of the designated imported merchandise and other (substituted) merchandise (see 19 U.S.C. 1313(b)); or
(ii) The fact and date(s) of manufacture or production of the exported or destroyed articles (see 19 U.S.C. 1313(a) and (b)).
(d) Approval of other accounting methods.
(1) Persons proposing to use an accounting method for identification of merchandise or articles for drawback purposes which has not been previously approved for such use (see paragraph (c) of this section), or which includes modifications from the methods listed in paragraph (c) of this section, may seek approval by CBP of the proposed accounting method under the provisions for obtaining an administrative ruling (see part 177 of this chapter). The conditions applied and the criteria used by CBP in approving such an alternative accounting method, or a modification of one of the approved accounting methods, will be the criteria in paragraph (b) of this section, as well as those in paragraph (d)(2) of this section.
(2) In order for a proposed accounting method to be approved by CBP for purposes of this section, it must meet the following criteria:
(i) For purposes of calculations of drawback, the proposed accounting method must be either revenue neutral or favorable to the Government; and
(ii) The proposed accounting method should be:
(A) Generally consistent with commercial accounting procedures, as applicable for purposes of drawback;
(B) Consistent with inventory or material control records used in the ordinary course of business by the person proposing the method; and
(C) Easily administered by CBP.
19 CFR Part 190 – Modernized Drawback”
https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-19/chapter-I/part-190
Claim Your Direct Identification Duty Drawback
No cost or obligation and easy to get started with Alliance. Identify new drawback program opportunity or evaluate the performance of your current program and maximize drawback refunds compliantly.
